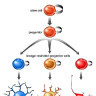
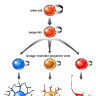
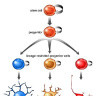
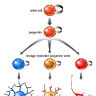
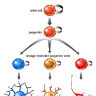
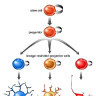
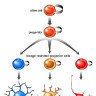
The ventricular zone is the place where cortical neurons are generated. It is located next to the ventricles. At first, this zone contains "progenitor" cells, which divide to produce neurons and glial cells. The glial fibers produced in the first divisions of progenitor cells are radially oriented, spanning the thickness of the cortex from the ventricular zone to the outer, pial surface, and provide scaffolding for the migration of neurons outwards from the ventricular zone.
The first divisions of the progenitor cells are symmetric, which duplicates the total number of progenitor cells at each mitotic cycle. Then, some progenitor cells begin to divide asymmetrically, producing one postmitotic cell that migrates along the radial glial fibers, leaving the ventricular zone, and one progenitor cell, which continues to divide until the end of development, when it differentiates into a glial cell or an ependymal cell. The migrating daughter cells become the pyramidal cells of the cerebral cortex.
- Part of Speech: noun
- Industry/Domain: Science
- Category: Basic science
Other terms in this blossary
Creator
- Barbara 60
- 100% positive feedback