asymmetric cell division
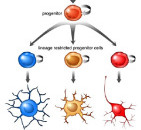
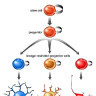
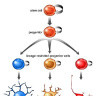
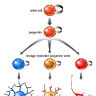
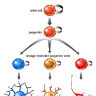
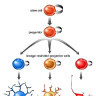
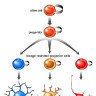
Stem cells can divide asymmetrically to self-renew whilst also producing differentiating daughter cells.
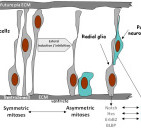
In the early mammalian cerebral cortex, neuroepithelial cells divide symmetrically to rapidly expand a stem cell pool. Later, neuroepithelial cells convert to radial glial cells, the major stem cell type contributing to cortical neurogenesis. Radial glial cells can divide asymmetrically to generate neurons either directly or via an intermediate basal progenitor cell.
The transition from symmetric to asymmetric division must be tightly regulated, as excessive symmetric cell division can lead to tumorous overgrowth, whereas precocious asymmetric division results in premature differentiation and underdeveloped organs.
- Part of Speech: noun
- Industry/Domain: Science
- Category: Basic science
0
Other terms in this blossary
Creator
- Barbara 60
- 100% positive feedback