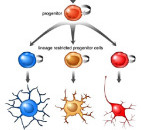
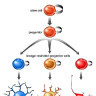
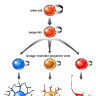
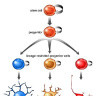
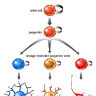
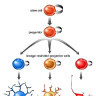
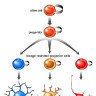
Neuroepithelial cells are the "stem cells" of the nervous system, deriving from actual stem cells in several different stages of neural development. These neural stem cells then differentiate further into multiple types of cells, like neurons, astrocytes and other glial cells. They appear during embryonic development of the neural tube as well as in adult neurogenesis in specific areas of the central nervous system.
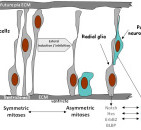
Neuroepithelial cells are capable of generating the first group of neurons in the neocortex and radial glial cells, the major neural progenitor cells responsible for producing neurons and glia. In the mouse neocortex, the transition of neuroepithelial cells to radial glial cells appears to occur around embryonic day 9.5–10.5 (E9.5–E10.5).
This transition is characterized by the initiation of the expression of astroglial markers such as astrocyte-specific glutamate transporter, SLC1A3, formerly known as GLAST and fatty acid binding protein 7 (FABP7) and an alteration in tight junctions including loss of Occludin.
- Part of Speech: noun
- Industry/Domain: Science
- Category: Basic science
Other terms in this blossary
Creator
- Barbara 60
- 100% positive feedback