Created by: pmss1990
Number of Blossarys: 1
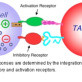
A type of lymphocyte and a component of innate immune system. It plays a major role in the host-rejection of both tumours and virally infected cells.
Hemoglobin-containing blood cell that transports oxygen from the lungs to tissues. In the tissues, the red blood cell exchanges its oxygen for carbon dioxide, which is brought back to the lungs to be ...
Any of a group of naturally occurring proteins that mediate communication between cells. Interleukins regulate cell growth, differentiation, and mobility. They are particularly important in ...
X-linked diseases are single gene disorders that reflect the presence of defective genes on the X chromosome. This chromosome is present as two copies in females but only as one copy in males.
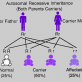
A genetic condition that appears only in individuals who have received two copies of an autosomal gene, one copy from each parent. The gene is on an autosome, a nonsex chromosome.
A lymphophenic form of congenital immunologic deficiency and thymic hypoplasia which was first described by Glanzmann and Riniker in 1950. Subsequent detailed clinical, pathologic, and immunologic ...
Autosomal recessive disorder. Both parents need to pass the defective gene to their child in order for that child to inherit the deficiency.


 English (EN)
English (EN)