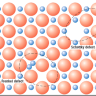
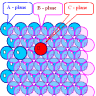
Two-dimensional Defects
The two-dimensional defects that appear in crystals can be usefully divided into
three types: free surfaces, which are the external surfaces at which the solid terminates at
a vapor or liquid, intercrystalline boundaries, which separate grains or distinct phases
within the solid, and internal defects that disrupt the crystalline pattern over a surface
within a crystal. All of these defects have two important characteristics. First, since they
are surfaces in a crystal they have particular atomic structures that depend on orientation.
Second, they have a positive energy. The energy per unit area is ordinarily equal to the
surface tension, ß, of the interface.
- Part of Speech: proper noun
- Industry/Domain: Materials science; Engineering
- Category: Metallurgy; Mechanical engineering
0
Creator
- Naveed
- 100% positive feedback
(Multan, Pakistan)